Friday, April 25, 2014
Monday, March 31, 2014
Wednesday, March 19, 2014
Linear Programming
Vertices:
|
||||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=3X+4Y
|
|||||||
x ≥
0
y ≥
0
x + y ≤ 6
|
C=0 |
|||||||
Vertices:
|
(5,8)
|
(5,4)
|
||||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C = 2x+ 5y
|
|||||||
x ≤ 5
y ≥ 4
-2x + 5y ≤ 30
|
C = 2(-5)+5(4)
C=10 |
C =2(5)+5(8)
C=50 |
C =2(5)+5(4)
C=30 |
|||||
Vertices:
|
(1,8)
|
(1,2)
|
(5,2)
|
|||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=7x+3y
|
|||||||
x ≥ 1
y ≥ 2
x + y ≤ 5
|
C=7(1)+3(8)
C=31 |
C=7(1)+3(2)
C=13 |
C=7(5)+3(2)
C=41 |
|||||
Vertices:
|
(0,8)
|
(0,4)
|
(6,8)
|
|||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C=4x+6y
|
|||||||
x ≥ 0
y ≤ 8
-2x + 3y ≥ 12
|
C=4(0)+6(8)
C=48 |
C=4(0)+6(4)
C=24 |
C=4(6)+6(8)
C=72 |
|||||
Vertices:
|
(0,4)
|
(0,0)
|
(2,3)
|
(5,0)
|
||||
Constraints
|
Objective Function: C= 8x + 7y
|
|||||||
x ≥ 0
y ≥ 0 4x+4y ≤ 20 x + 2y ≤ 8 |
C= 8(0) + 7(4)
C= 28 |
C= 8(0)+7(0)
C= 0 |
C= 8(2)+7(3)
C= 37 |
C=8(5)+7(0)
C=40 |
||||
Wednesday, March 12, 2014
Graphing Exponential Equations
Graphing Exponential Growth/Decay
0<a<1 = compression
a< 0(negative) = flipped over x-axis.
1. Create the Parent Graph.
2. Identify A,H,K.
3. Create your new T-Chart.
- Domain: All real #'s.
- Range: y>k; when a is positive. y<k; when a is negative.
- Asymptote: y=k.
4. Draw Asymptote
5. Graph new points.
- Exponential Formula: y=a×bx-h+k
- a = multiplier.
0<a<1 = compression
a< 0(negative) = flipped over x-axis.
0<b<1 = fraction; decay, always decreasing.
B is never negative only the multiplier is.
- h = lf/rt; opposite
- k = up/dn
Compound Interest Formula
Compound Interest: Interest calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan.
A = amount of money accumulated after n years, including interest.
P = principal amount (the initial amount you borrow or deposit)
r = annual rate of interest (as a decimal)
t = number of years the amount is deposited or borrowed for.
n = number of times the interest is compounded per year
Monday, March 10, 2014
Friday, February 21, 2014
Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
A Sequence is a set of numbers that are in order.
- In an Arithmetic Sequence the difference between one term and the next is you just add the same value each time.
an = a1 +(n - 1)
General Form of an Geometric Sequence
an = a1·rn-1
d = the common difference
a1 = the first number in the sequence
n = the number of the place of the sequence you're trying to figure out
n = the number of the place of the sequence you're trying to figure out
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
Characteristics and traits
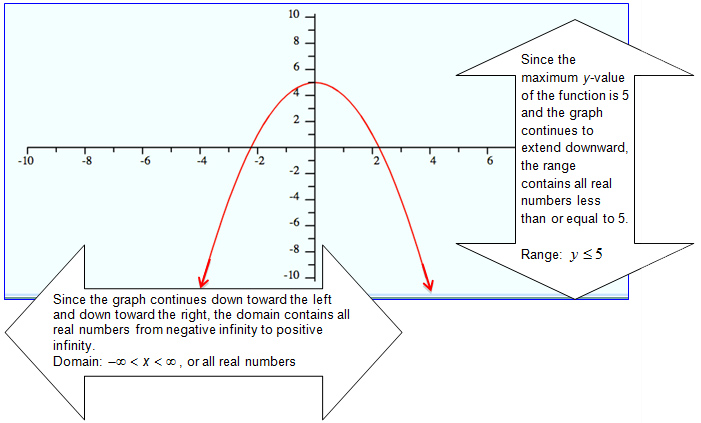
Domain- Describing left/right of a graph (x-values)
Range- Describing up/down of a graph (y-values)
End behavior- Describing the 2 ends of an equation
Absolute max/min- The 1 point that is the highest on a graph (x,y)
Local max/min- More than one point that are the highest/ lowest points
Interval of increase- Section of a graph where y values are increasing
Interval of decreasing- Section of graph where y values decrease
Symmetry-
Even symmetry- symmetric about y axis
Odd symmetry- symmetric about x origin
Neither- no symmetry
One to one- Passes vertical/horizontal line test
Function- Passes vertical line test

Asymptotes- Curve in a line, line that gets close to the line but never touches it
X intercept- (a,0) crosses x axis
Y intercept- (0,b) crosses y axiz
Range- Describing up/down of a graph (y-values)
End behavior- Describing the 2 ends of an equation
Absolute max/min- The 1 point that is the highest on a graph (x,y)
Local max/min- More than one point that are the highest/ lowest points
Interval of increase- Section of a graph where y values are increasing
Interval of decreasing- Section of graph where y values decrease
Symmetry-
Even symmetry- symmetric about y axis
Odd symmetry- symmetric about x origin
Neither- no symmetry
One to one- Passes vertical/horizontal line test
Asymptotes- Curve in a line, line that gets close to the line but never touches it
X intercept- (a,0) crosses x axis
Y intercept- (0,b) crosses y axiz
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)